Java集合是针对所有数据操作作业的一站式解决方案,例如存储数据、搜索、排序、插入、删除和更新数据。Java集合作为单个对象进行响应,Java集合框架提供各种接口和类。
什么是Java集合?
Java集合是一种预定义的体系结构,能够存储一组元素,其行为类似于单个单元,如对象或组。
什么是Java集合框架?
Java集合框架为Java集合提供了在类和接口中表示一组元素的能力。
Java集合框架使用户能够执行各种数据操作,如存储数据、搜索、排序、插入、删除和更新元素组上的数据。
Java集合框架层次结构
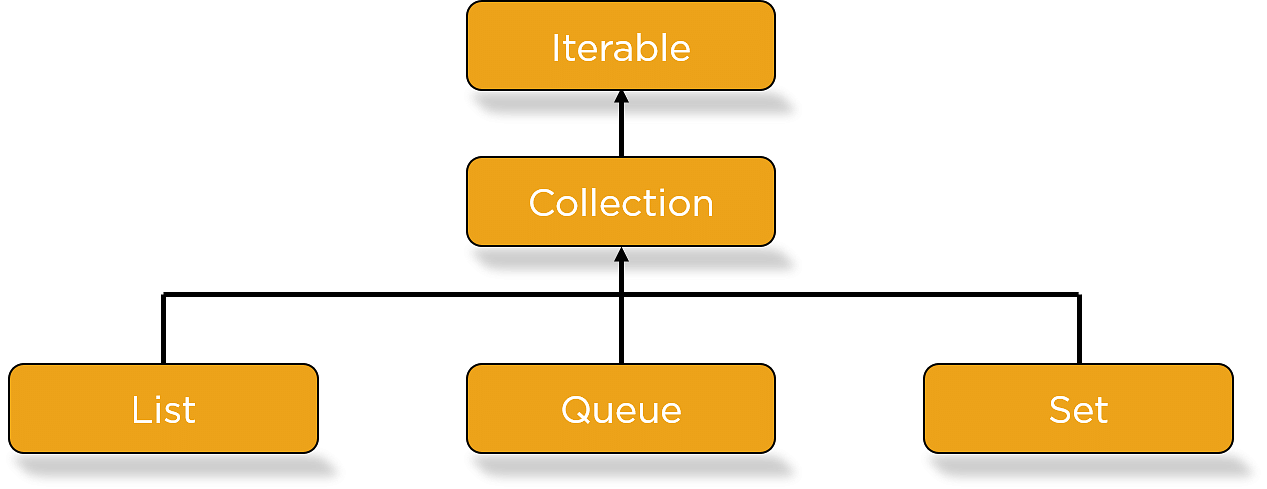
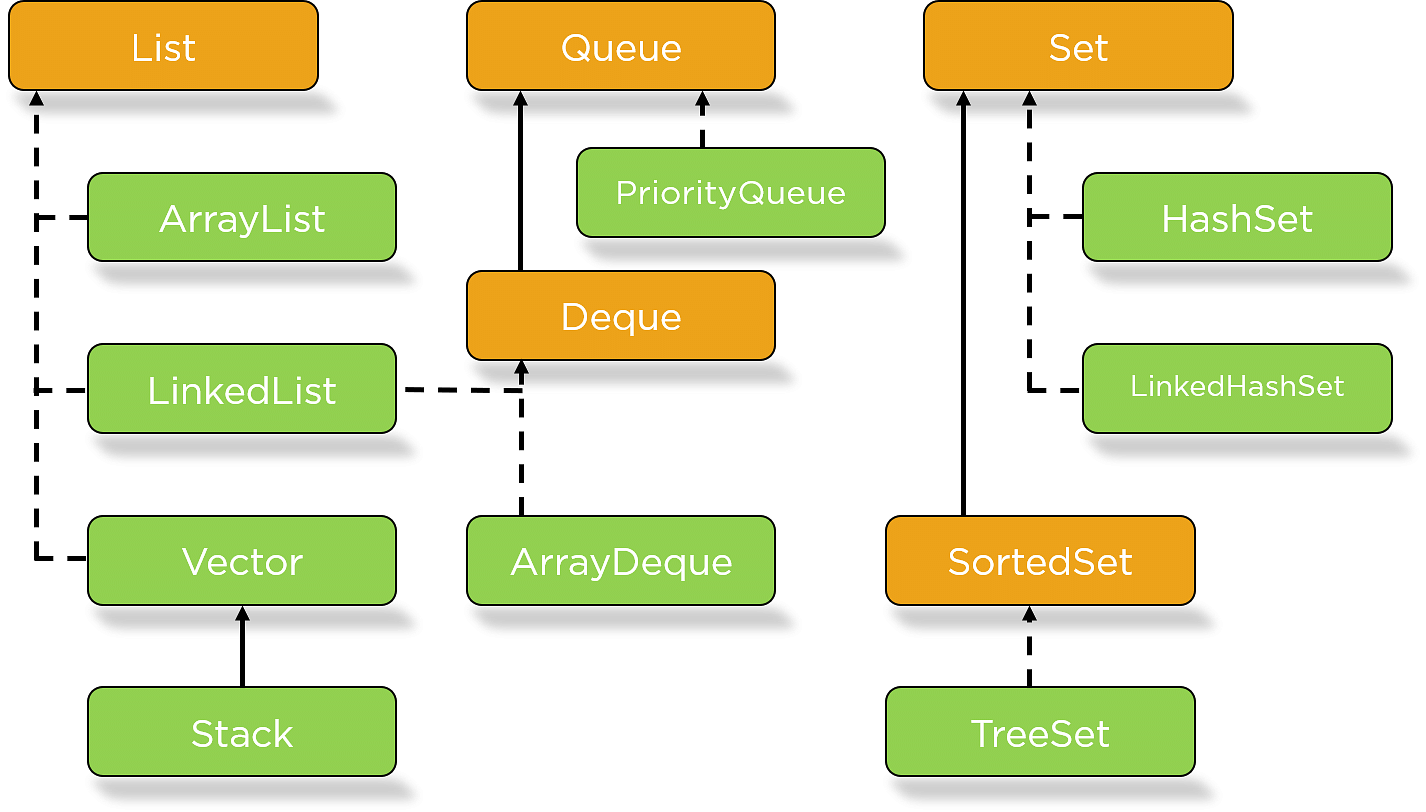
下图描述了Java集合层次结构。
了解了Java集合的层次结构之后,您还应该了解应用于Java中的集合以执行数据操作操作的各种方法。
Java集合接口方法
下表介绍了可用于数据操作作业的Java集合的方法。
Java集合接口
Set Interface
Set接口继承自Java集合接口Set接口不能在其中存储重复/冗余元素。下面是一个基于Set接口的示例。
Example:
//Set Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
public class SetExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int count[] = { 21, 23, 43, 53, 22, 65 };
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
try {
for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
set.add(count[i]);
}
System.out.println(set);
TreeSet<Integer> sortedSet = new TreeSet<Integer>(set);
System.out.println("The sorted list is:");
System.out.println(sortedSet);
System.out.println("First element of the set is: " + (Integer) sortedSet.first());
System.out.println("last element of the set is: " + (Integer) sortedSet.last());
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
List Interface
List接口是从Java Util包派生的。该列表使用户能够在索引方法的帮助下维护元素的有序集合,并可以执行数据操作操作,如插入、更新、删除等。例如:
Example:
//List Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
public class ListInterface {
public static void main(String args[]) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("David");
list.add("Jhon");
list.add("Stacy");
//list.add("Stacy");
for (String Students : list)
System.out.println(Students);
}
}
Queue Interface
队列接口继承自Java集合接口。队列是一个线性集合,它提供对集合元素的数据操作,并遵循FIFO(先进先出)原则。例如:
Example:
//Queue Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
public class QueueInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add("Apple");
queue.add("Mango");
queue.add("Grapes");
queue.add("Banana");
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove("Grapes");
System.out.println(queue);
System.out.println("Queue total Size: " + queue.size());
System.out.println("Queue includes fruit 'Apple'? : " + queue.contains("Apple"));
queue.clear();
}
}
Deque Interface
Deque接口继承自Java Collections接口。DE-Que是Double-Ended Queue的缩写。Deque支持队列两端的插入和删除操作。
Example:
//Deque Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class DequeInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> num = new ArrayDeque<>();
num.offer(10);
num.offerLast(21);
num.offerFirst(52);
System.out.println("Deque elements: " + num);
int first = num.peekFirst();
System.out.println("First Element is: " + first);
int lastElement = num.peekLast();
System.out.println("Last Element: " + lastElement);
int removed = num.pollFirst();
System.out.println("Removed First Element: " + removed);
System.out.println("Updated Deque is: " + num);
}
}
Map Interface
Map接口继承自Java集合接口。映射不能存储重复元素。映射使用键-值对格式存储数据。操作操作通过访问键-值对来处理。
Example:
//Map Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class MapInterface {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Map<Integer, String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1, "Cricket");
map.put(2, "Hockey");
map.put(3, "Archery");
for (Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Entry<Integer, String> m = iterator.next();
System.out.println(m.getKey() + " " + m.getValue());
}
}
}
SortedSet Interface
排序集接口按升序维护映射。它们用于自然有序的收集。
An example of SortedSet Interface:
//Sortedset Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
public class SortedSetInterface {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SortedSet set = new TreeSet();
set.add("Bob");
set.add("Sean");
set.add("Jennifer");
Iterator i = set.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Object element = i.next();
System.out.println(element.toString());
}
}
}
SortedMap Interface
排序后的映射界面按临界升序维护元素的映射。SortedMap是SortedSet的Map模拟。
Example:
//Sortedmap Interface
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
public class SortedMapInterface {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeMap<String, Double> t = new TreeMap<String, Double>();
t.put("John", new Double(76.5));
t.put("Molley", new Double(87.3));
t.put("Aron", new Double(78.2));
t.put("Daisy", new Double(73.4));
Set<?> set = t.entrySet();
Iterator<?> i = set.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()) {
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Map.Entry me = (Map.Entry)i.next();
System.out.print(me.getKey() + ": ");
System.out.println(me.getValue());
}
System.out.println();
double percentage = ((Double)t.get("Molley")).doubleValue();
t.put("Molley", new Double(percentage));
System.out.println("Zara's new balance: " + t.get("Molley"));
}
}
在此之后,我们将讨论另一个关键方面,Java集合的一个相邻分支,称为Java集合类。
Java集合类
HashSet类
HashSet类继承自AbstractSet类。HashSet类使用Hash表存储元素。HashSet允许空元素,并且不遵循任何顺序来存储元素。
//HashSet Class
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class HashSetClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
HashSet<String> hset = new HashSet<String>();
hset.add("Suzuki");
hset.add("Kawasaki");
hset.add("Honda");
hset.add("Ducati");
hset.add("Yamaha");
hset.add("Yamaha");
hset.add("Suzuki");
hset.add(null);
hset.add(null);
// 显示HashSet元素
System.out.println(hset);
}
}
TreeSet类
TreeSet类是一个基于TreeMap的NavigableSet实现。在这里,使用比较器对元素进行排序。
//TreeSet
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class TreeSetClass {
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeSet<Integer> treeset = new TreeSet<Integer>();
treeset.add(8476);
treeset.add(748);
treeset.add(88);
treeset.add(983);
treeset.add(18);
treeset.add(0);
System.out.println(treeset);
}
}
ArrayList类
Java中的ArrayList是一个可调整大小的数组,它是允许空元素的ListInterface的实现。ArrayList有三种不同类型的数组,如下所示。
一维数组
二维数组
多维数组
相关阅读: # Java 中的数组:声明、定义和访问数组
一维数组
一维数组有一行按地址的顺序排列元素,如下图所示。

//One-Dimensional Array
package tech.besthub;
public class OneDA {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] a = new int[3];
a[0] = 10;
a[1] = 20;
a[2] = 30;
System.out.println("One dimensional array");
System.out.println(a[0]);
System.out.println(a[1]);
System.out.println(a[2]);
}
}
二维数组
二维数组有行和列。它以矩阵的形式排列元素,如下图所示。
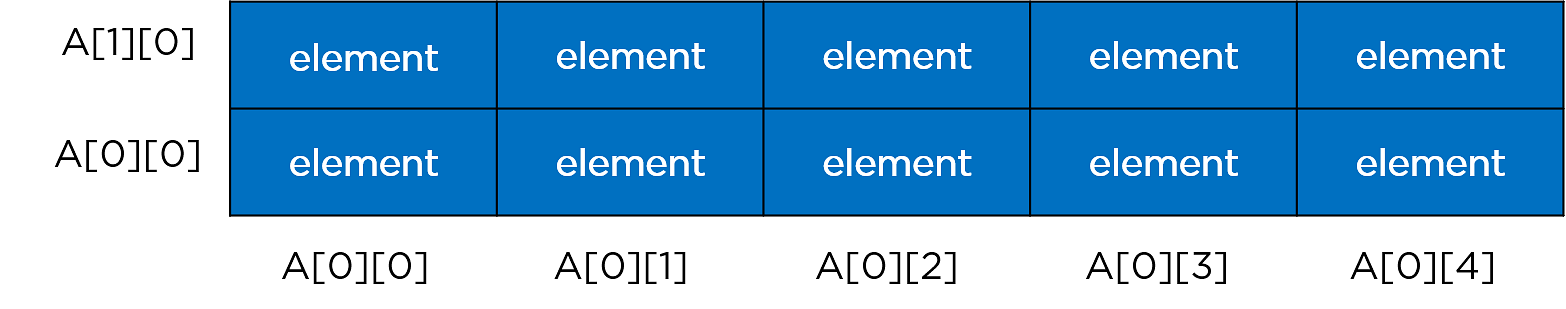
Example:
//Two-Dimensional Array
package tech.besthub;
public class TwoDA {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++)
System.out.println("arr[" + i + "][" + j + "] = " + arr[i][j]);
}
}
多维数组
多维数组是多个二维数组的组合;它看起来像一个3-D图像,如下所示
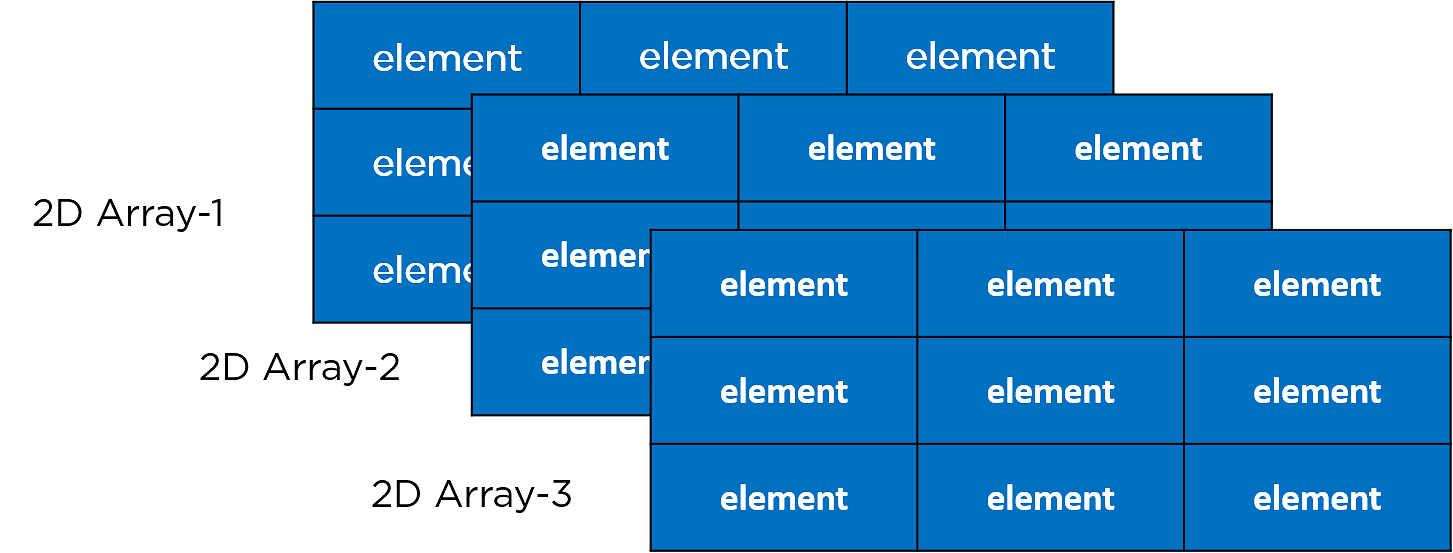
Example:
//Three/Multi-Dimensional Array
package tech.besthub;
public class ThreeDA {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int A[][] = { { 1, 2, 3 }, { 4, 5, 6 }, { 7, 8, 9 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(A[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
LinkedList类
LinkedList类是List和Dque接口的实现。链表类似于数组,但它不按顺序数据地址存储数据,而是按顺序连接内存块,并允许空元素。
有三种不同类型的链表。
单链表
双向链表
循环链表
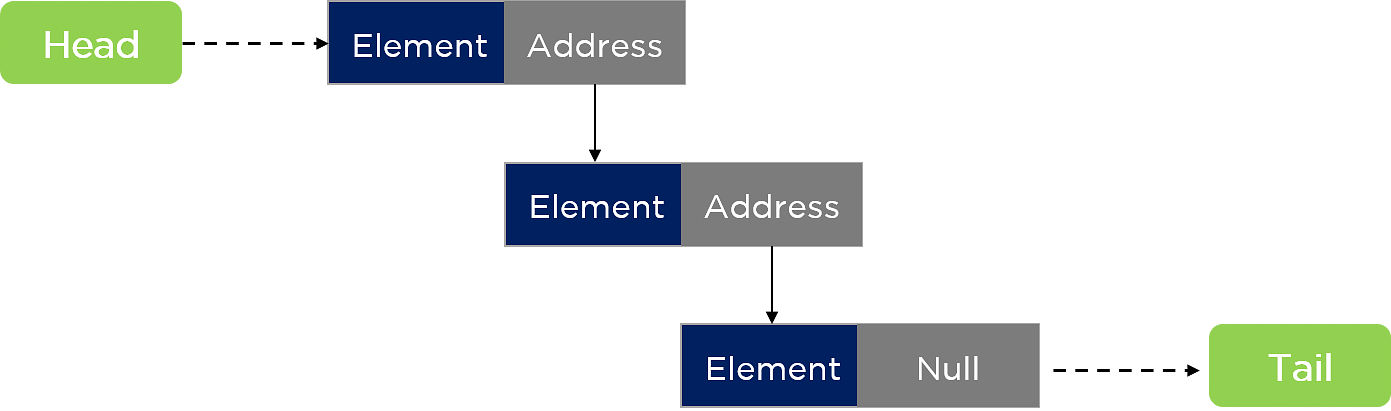
单链表
单链表将元素存储在不同的内存位置,然后在一个方向上连接它们以按顺序表示它们。下图显示了一个典型的单链表。
单向链表只提供单向遍历。
//Singly-LinkedList
package tech.besthub;
public class SiinglyLinkedList {
Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
public void display() {
Node n = head;
while (n != null) {
System.out.print(n.data + " ");
n = n.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SiinglyLinkedList list = new SiinglyLinkedList();
list.head = new Node(1);
Node second = new Node(2);
Node third = new Node(3);
Node fourth = new Node(4);
list.head.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
list.display();
}
}
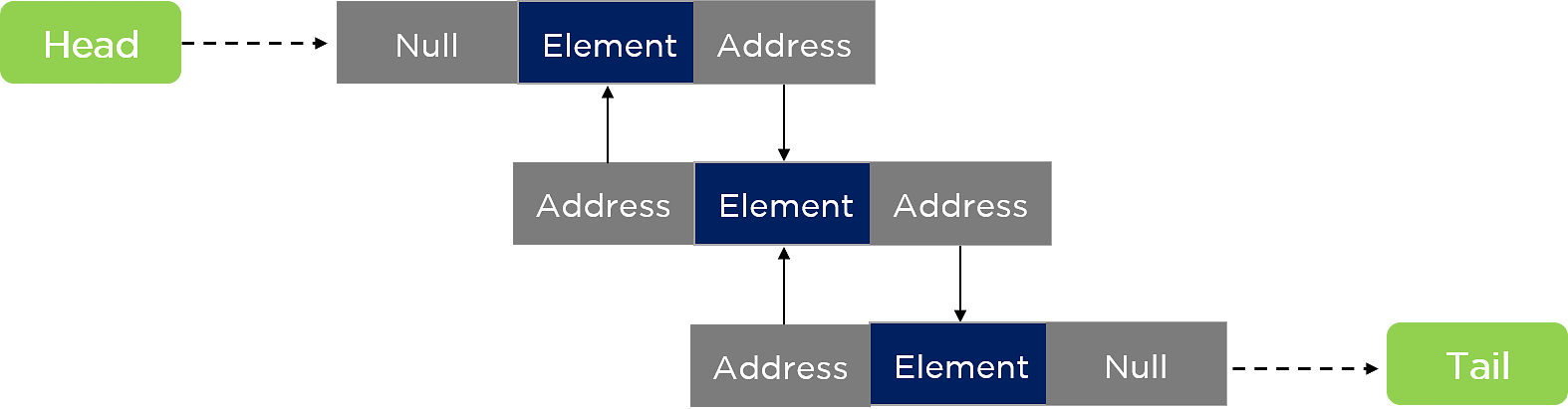
双向链表
双向链表通常是单向链表,但双向链表提供双向遍历。下面是一个典型的双向链表的外观:
Example:
//Doubly LinkedList
package tech.besthub;
public class DoublyLinkedList {
class Node {
int data;
Node previous;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
Node head, tail = null;
public void addNode(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
head.previous = null;
tail.next = null;
} else {
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.previous = tail;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = null;
}
}
public void display() {
Node current = head;
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
return;
}
System.out.println("Nodes of doubly linked list: ");
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList dList = new DoublyLinkedList();
dList.addNode(1);
dList.addNode(2);
dList.addNode(3);
dList.addNode(4);
dList.addNode(5);
dList.display();
}
}
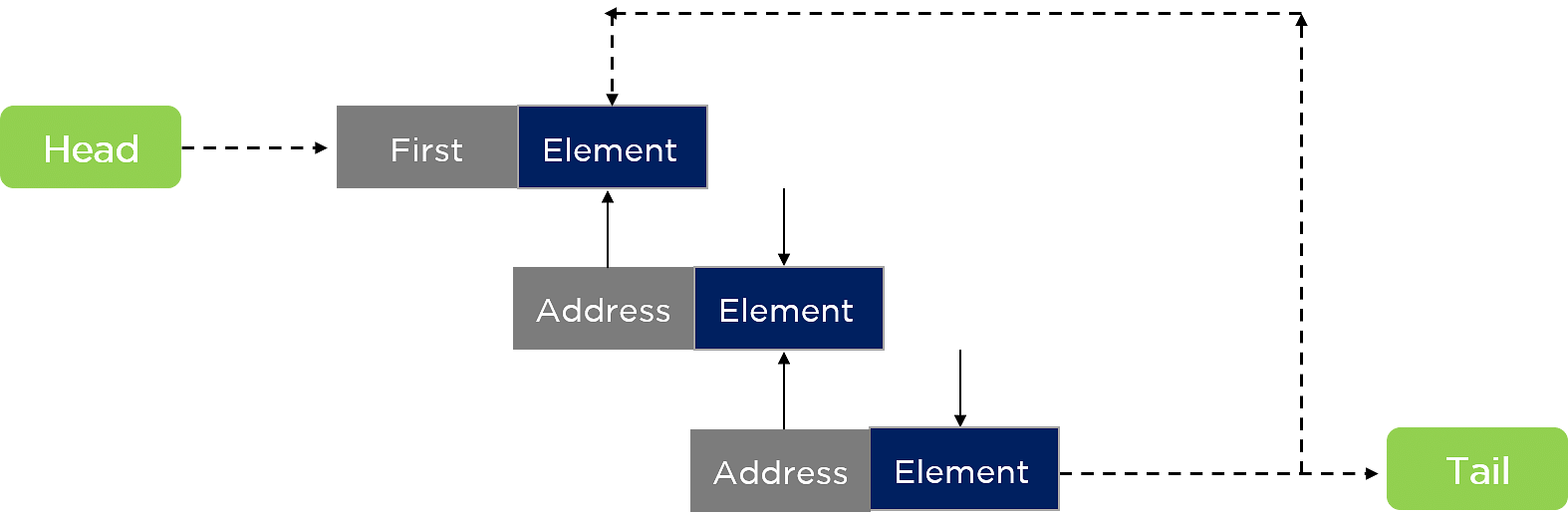
循环链表
循环链表是一种典型的单链表。唯一的变化是循环链表的末端/尾部指向链表的头节点。最后的头和尾连接使循环链表提供循环遍历。
Example:
//Circular LinkedList
package tech.besthub;
public class CLL {
public class Node{
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public Node head = null;
public Node tail = null;
public void add(int data){
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if(head == null) {
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
newNode.next = head;
}
else {
tail.next = newNode;
tail = newNode;
tail.next = head;
}
}
public void display() {
Node current = head;
if(head == null) {
System.out.println("List is empty");
}
else {
System.out.println("Nodes of the circular linked list: ");
do{
System.out.print(" "+ current.data);
current = current.next;
}while(current != head);
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
CLL c = new CLL();
c.add(1);
c.add(2);
c.add(3);
c.add(4);
c.add(5);
c.add(6);
c.add(7);
c.add(8);
c.display();
}
}
HashMap类
HashMap派生自Map接口。HashMap使用键-值对方法存储数据。HashMap不允许重复元素。
//HashMap Class
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String, String> Make = new HashMap<String, String>();
Make.put("Honda", "CBR");
Make.put("Kawasaki", "Ninja");
Make.put("Ducati", "Panigale");
Make.put("Yamaha", "R1");
System.out.println(Make);
}
}
TreeMap类
树图派生自AbstractMap类。TreeMap以键-值对的形式存储元素。TreeMap不允许集合中存在空值和重复值。
Example:
//TreeMap Class
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class TreeMapClass{
public static void main(String args[]){
TreeMap<Integer,String> map=new TreeMap<Integer,String>();
map.put(2019901,"Amber");
map.put(2019902,"james");
map.put(2019903,"Violet");
map.put(2019904,"Reynolds");
for (Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
Entry<Integer, String> m = iterator.next();
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue());
}
}
}
集合API算法
Java集合API算法提供了在搜索、排序和其他作业中常用的实现。
Sorting
排序算法是集合API算法之一。排序算法根据用户编写的修改按升序或降序对元素进行排序。

Example:
//Bubble Sort
package tech.besthub;
public class BubbleSort {
static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
int temp = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < (n - i); j++) {
if (arr[j - 1] > arr[j]) {
temp = arr[j - 1];
arr[j - 1] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int arr[] = { 289, 39, 48, 6, 28, 1, 2, 33 };
System.out.println("Array Before Bubble Sort");
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
bubbleSort(arr);
System.out.println("Array After Bubble Sort");
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[j] + " ");
}
}
}
Shuffling
随机算法是集合API算法之一。混洗算法的功能是破坏当前的安排。他们被用来在列表中制造随机性。
Example:
//Shuffle algorithm
package tech.besthub;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class Shuffle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] intA = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100 };
List<Integer> intL = Arrays.asList(intA);
Collections.shuffle(intL);
intL.toArray(intA);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(intA));
}
}
Searching
基于所使用的搜索机制的类型,使用搜索算法来搜索列表/数组中的元素。

Example:
//Binary Search
package tech.besthub;
public class BinarySearch1 {
public static int binarySearch(int arr[], int first, int last, int key) {
if (last >= first) {
int mid = first + (last - first) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == key) {
return mid;
}
if (arr[mid] > key) {
return binarySearch(arr, first, mid - 1, key);
} else {
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, last, key);
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int k = 2;
int last = arr.length - 1;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, last, k);
if (result == -1)
System.out.println("Element is not found!");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at index: " + result);
}
}
Composition
频率和不相交算法检查一个或多个集合的组成的几个方面。

构图分为两部分:
频率:检查重复元素的计数
不相交:确保没有重复的元素
Example:
//Composition
package tech.besthub;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Book {
public String title;
public String author;
Book(String title, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
}
class Library {
// reference to refer to list of books.
private final List<Book> books;
Library(List<Book> books) {
this.books = books;
}
public List<Book> getTotalBooksInLibrary() {
return books;
}
}
public class Composition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book b1 = new Book("EffectiveJ Java", "Joshua Bloch");
Book b2 = new Book("Thinking in Java", "Bruce Eckel");
Book b3 = new Book("Java: The Complete Reference", "Herbert Schildt");
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
books.add(b1);
books.add(b2);
books.add(b3);
Library library = new Library(books);
List<Book> bks = library.getTotalBooksInLibrary();
for (Book bk : bks) {
System.out.println("Title : " + bk.title + " and " + " Author : " + bk.author);
}
}
}
Java集合的好处
软件/代码可重用性
Java集合无可挑剔地减少了代码行,并以最可靠的方式实现了代码可重用性。
易于设计API
预定义的Java集合算法API大大减少了时间。如果没有这些API,将导致为简单的排序操作编写数小时的代码。
更易于学习和使用新的API
预定义API的使用使学习过程变得更加直接和有用。
提高编程速度
Java集合引入的简化减少了程序员的工作量。编码过程的简单性反过来又导致了最有效和最高效的编程做法,从而节省了时间。

