Java 字符串通常是一种数据类型,但通常被视为一种数据结构,因为它按顺序存储字符类型的元素,就像数组一样。在本文中,我们将通过以下摘要直接了解有关Java字符串的所有内容。
什么是 Java 字符串?
我们可以将Java字符串定义为Java中专用于顺序存储字符的对象。
例如:
char[] S ={'S', 'i', 'm', 'p', 'l', 'i', 'l', 'e', 'a', 'r', 'n'} ;
String str=new String(S);
//or
String S = "BestHub";
现在我们已经了解了 Java 字符串的定义及其示例,让我们继续了解如何实时创建 Java 字符串。
如何创建 Java 字符串?
我们可以通过两种不同的方式创建 Java 字符串。我们将通过示例来学习它们,以获得更完善的学习体验。
方法一 - 字符串文字
Java 字符串可以按照下面给出的语法使用字符串文字方法创建。
String str = "Hello World";
在此方法中,必须使用双引号 (")。
每当您传递使用文字字符串方法创建新字符串的命令时,Java 虚拟机 (JVM) 都会在字符串池中搜索该字符串。如果该字符串存在,那么 JVM 将返回对该字符串的引用。
如果字符串池中不存在所需的字符串,则 JVM 将根据用户的命令创建新的字符串。
方法二 - 新建关键字
在第二种方法中,我们使用关键字“new”来创建一个新字符串。我们将遵循下面提到的语法来创建一个唯一的字符串。
String str = new String("Hello World")
这里将使用堆内存创建字符串 str。然而,文字“Hello World”存储在字符串池中。
现在,我们已经了解了 Java 字符串以及如何使用两种不同的方法及其语法来创建它们。接下来,我们将了解 Java 字符串接口。
Java 字符串接口
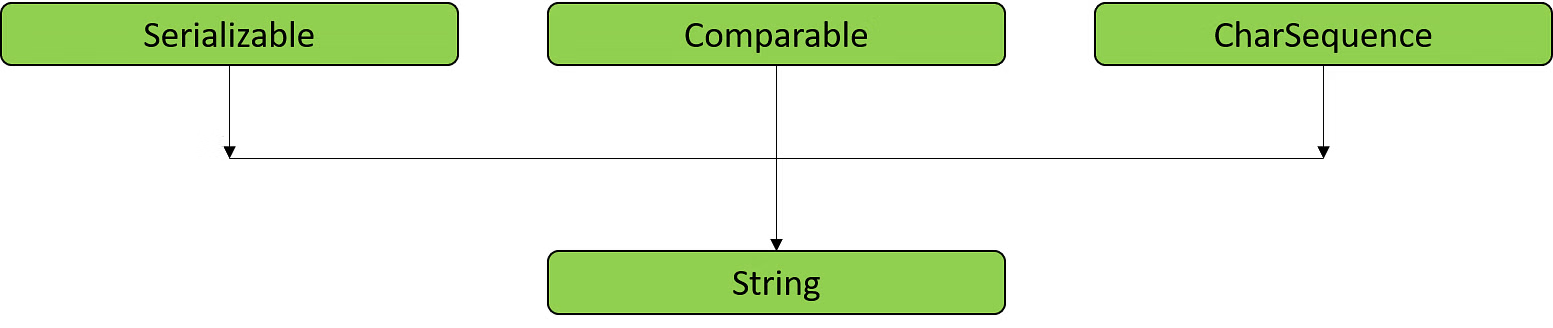
Java 字符串来自 java.lang.String 类。Java Strings 能够执行各种字符串操作操作。为此,java.lang.String 类实现了三个接口,如下所述。
可串行化
可比
字符序列
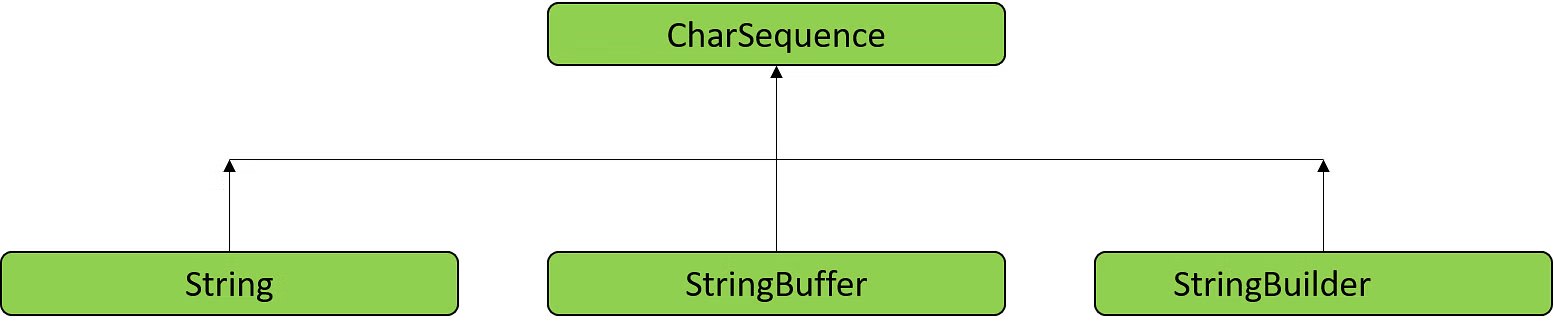
要创建新字符串,我们需要 String 一个 StringBuilder 和 StringBuffer。StringBuffer 和 StringBuilder 实现了 CharSequence 以在 Java 中创建新字符串。
遵循 Java 字符串的基础知识,我们将继续讨论 Java 字符串可用的方法。
Java 字符串中的方法
以下是 Java 中可用的主要方法。
String charAt()
string charAt() 方法专用于返回整个字符串中选定索引号的 char 值。
句法:public char charAt(int index)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String name = "BestHub";
char ch = name.charAt(5);
System.out.println(ch);
}
}
String compareTo()
Sting的compareTo方法用于按字典顺序比较两个字符串。
如果比较结果为正数,则给定 String 按字典顺序大于当前 String。
如果比较结果为负,则给定数字按字典顺序小于当前字符串。
如果比较为零,则给定数字按字典顺序等于当前字符串。
句法:
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Simple";
String s2 = "BestHub";
String s3 = "BestHub";
String s4 = "Learn";
String s5 = "E-Learning";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));
System.out.println(s2.compareTo(s3));
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s4));
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s5));
}
}
String concat()
String concat() 方法用于组合两个不同的字符串。在这里,第二个字符串连接到第一个字符串的末尾。
句法:
public String concat(String secondString)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub ";
s1.concat("Best in class");
System.out.println(s1);
s1 = s1.concat("Best in class E-Learning Platform");
System.out.println(s1);
}
}
String contain()
String contains() 方法用于搜索给定 String 中的特定字符或字符串段。如果找到搜索关键字,该方法返回 true;如果未找到,则返回负值。
句法:public boolean contains(CharSequence search_keyword)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "BestHub E-Learning Platform";
boolean isContains = str.contains("BestHub");
System.out.println(isContains);
System.out.println(str.contains("Simple"));
}
}
String endsWith()
StringendsWith() 方法用于检查字符串是否以特定字符或一组字符结尾。如果当前 String 以给定的字符/字符串结尾,则该方法返回 true;否则,该方法将返回 false。
句法:public boolean endsWith(String suffixString)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World. Welcome to BestHub'';
System.out.println(s1.endsWith("BestHub"));
}
}
String equals()
String equals() 方法用于比较当前 String 与给定 String 并检查它们是否相等。如果两者匹配,则该方法返回 true;如果不匹配,则返回 false。
句法:public boolean equals(Object givenObject)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "HelloWorld";
String s2 = "HelloWorld";
String s3 = "Welcome to BestHub";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
}
}
String format()
String format() 方法用于打印给定字符串的格式化版本。用户需要使用 String.format() 方法,否则默认会调用 Locale.getDefault() 方法。
句法:public static String format(String format, strings, args)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String name = "BestHub";
String sf1 = String.format("String is %s", name);
String sf2 = String.format("value is %f", 14.1234);
String sf3 = String.format("value is %14.12f", 14.1234);
System.out.println(sf1);
System.out.println(sf2);
System.out.println(sf3);
}
}
String equalsIgnoreCase()
String equalsIgnoreCase() 方法也比较两个不同的字符串,就像 String equal() 方法一样。不过,区别在于区分大小写不被视为比较参数。
句法:public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String s)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub";
String s2 = "BestHub";
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));
}
}
String getBytes()
String getBytes() 方法用于获取给定 String 的字节数组。
句法:public byte[] getBytes(Charset charset)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub";
byte[] byteArray = s1.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < byteArray.length; i++) {
System.out.println(byteArray[i]);
}
}
}
String getChars()
getChars() 方法将给定 String 的内容复制到当前 char 数组中。
句法:public void getChars(int sourceBeginInd, int sourceEndInd, char[] destination, int destBeginInd)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String str = new String("Welcome to BestHub");
char[] ch = new char[10];
try {
str.getChars(5, 11, ch, 0);
System.out.println(ch);
} catch (Exception ex) {
System.out.println(ex);
}
}
}
String indexOf()
String indexOf() 方法用于返回给定字符串中所选字符的索引值。如果找到该字符,则该方法返回索引值。否则返回-1。
句法:int index= s1.indexOf("str");
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World, Welcome to BestHub";
int ind1 = s1.indexOf("World");
System.out.println(ind1);
int ind3 = s1.indexOf("to", 4);
System.out.println(ind3);
int index4 = s1.indexOf('S');
System.out.println(index4);
}
}
String intern()
String inter() 方法用于将给定字符串转换为内部字符串并返回字符串规范形式。
句法:public String intern()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = new String("BestHub");
String s2 = "BestHub";
String s3 = s1.intern();
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s2 == s3);
}
}
String isEmpty()
String isEmpty() 方法用于检查给定字符串是否为空。如果发现字符串为空,则该方法返回 true。如果不是,则该方法返回 false。
句法:public boolean isEmpty()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "";
String s2 = "BestHub";
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty());
System.out.println(s2.isEmpty());
}
}
String join()
String join() 方法用于在使用给定分隔符连接后返回给定字符串。
句法:public static String join(CharSequence delimiter, Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String joinString1 = String.join("-", "Welcome", "to", "BestHub");
System.out.println(joinString1);
}
}
String lastIndexOf()
string lastIndexOf() 方法旨在返回给定字符串的最后一个索引值。如果未找到,则该方法返回 -1。
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World. Welcome to BestHub";
int indexV = s1.lastIndexOf('S');
System.out.println(indexV);
}
}
String length()
String length() 方法用于找出给定字符串的大小。它计算给定字符串中可用的字符数。
句法:public int length()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub";
System.out.println("The length of the string is: " + s1.length());
}
}
String replace()
String Replace() 方法用于用新的 CharSequence 替换旧的 CharSequence 集。
句法:public String replace(char oldCharSeq, char newCharSeq)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World, Welcome to Java";
String replaceString = s1.replace('W', 'H');
System.out.println(replaceString);
}
}
String replaceAll()
string ReplaceAll() 方法旨在用匹配的正则表达式和替换字符串替换当前字符序列后返回一个字符串。
句法:public String replaceAll(String regex, String newString)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World Welcome to BestHub";
String replaceString = s1.replaceAll("l", "a");
System.out.println(replaceString);
}
}
String split()
string split() 方法用于使用给定的正则表达式拆分当前 String,然后返回一个新的 char 数组。
句法:public String split(String regex, int limit)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World Welcome to BestHub";
String[] words = s1.split("\\s");
for (String w : words) {
System.out.println(w);
}
}
}
String startsWith()
字符串startsWith()方法用于检查当前字符串是否以给定前缀开头。如果当前 String 以给定前缀开头,则该方法返回 true;该方法返回 false。
句法:public boolean startsWith(String prefixString)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "Hello World";
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("Hell"));
System.out.println(s1.startsWith("Java"));
}
}
String toCharArray()
String toCharArray() 方法用于将字符串转换为字符数组。新字符数组的索引值将与旧字符串的索引值相同。
句法:public char[] toCharArray()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub";
char[] ch = s1.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
}
}
String toUpperCase()
String toUpperCase() 方法用于将 String 小写转换为大写。
句法:public String toUpperCase()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub";
String s1upper = s1.toUpperCase();
System.out.println(s1upper);
}
}
String toLowerCase()
String toLowerCase() 方法用于将大写字符串转换为小写。
句法:public String toLowerCase()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = "BestHub";
String s1lower = s1.toLowerCase();
System.out.println(s1lower);
}
}
String trim()
Stringtrim() 方法用于删除给定字符串中不需要的前导和尾随空格。
句法:public String trim()
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
String s1 = " Hello World ";
System.out.println(s1.trim() + " Welcome to BestHub");
}
}
String valueOf()
String valueOf() 方法将不同的数字或任何数据类型值或元素转换为字符串。
句法:public static String valueOf(int i)
Example:
package tech.besthub;
public class BestHubString {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int value = 100;
String s1 = String.valueOf(value);
System.out.println(s1 + 299);
}
}
至此,我们就结束了这篇 Java 字符串文章。接下来,我们将研究您可以采取的下一个关键步骤来掌握 Java。

